
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АстрономияБиологияГеографияДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Plasticity
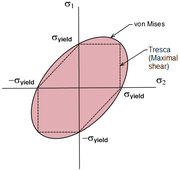 Comparison of Tresca and Von Mises Criteria
Comparison of Tresca and Von Mises Criteria
Some design is based on the assumption that materials will behave plastically.[27] A plastic material is one which does not obey Hooke's Law, and therefore deformation is not proportional to the applied load. Plastic materials are ductile materials. Plasticity theory can be used for some reinforced concrete structures assuming they are underreinforced, meaning that the steel reinforcement fails before the concrete does.
Plasticity theory states that the point at which a structure collapses (reaches yield) lies between an upper and a lower bound on the load, defined as follows:
If, for a given external load, it is possible to find a distribution of moments that satisfies equilibrium requirements, with the moment not exceeding the yield moment at any location, and if the boundary conditions are satisfied, then the given load is a lower bound on the collapse load.
If, for a small increment of displacement, the internal work done by the structure, assuming that the moment at every plastic hinge is equal to the yield moment and that the boundary conditions are satisfied, is equal to the external work done by the given load for that same small increment of displacement, then that load is an upper bound on the collapse load.
If the correct collapse load is found, the two methods will give the same result for the collapse load.[28]
Plasticity theory depends upon a correct understanding of when yield will occur. A number of different models for stress distribution and approximations to the yield surface of plastic materials exist:[29]
Mohr's circle
Von Mises yield criterion
Henri Tresca
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; просмотров: 286; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!; Нарушение авторских прав |